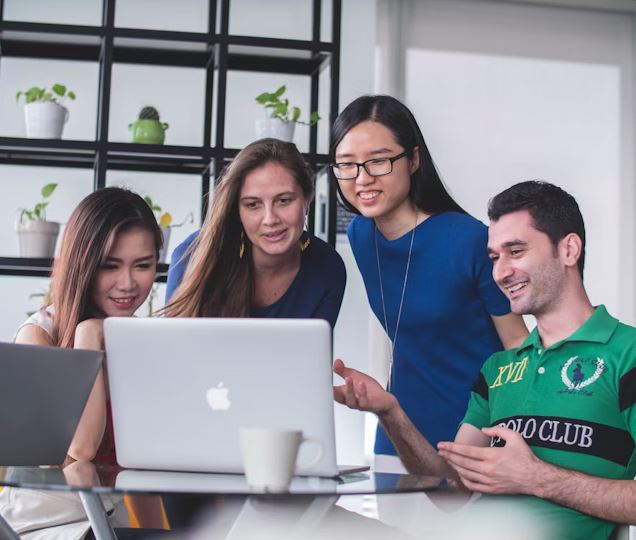
Cooped Up at Home? Help Scientists Spot Penguins from Space or Seek Out Galaxies

There are at the very least two bright spots in these strange situations: Telescopes are nevertheless learning distant galaxies and penguins are nevertheless pooping throughout Antarctica. In each conditions, if you’re hunting for new means to go the time whilst you keep residence, you can enable out experts learning these phenomena.
Citizen science is nothing at all new, but it’s a specially appealing selection as the spreading coronavirus prompts containment steps around the entire world. So if you’d like to acquire your intellect off latest functions for a whilst, contemplate chipping in on a exploration project.
“I feel wherever we can tap into people’s enthusiasm by means of their personal computer, that kind of captures the zeitgeist of coronavirus: what can we do when we’re all trapped at residence,” Heather Lynch, a statistical ecologist at Stony Brook College in New York, advised Place.com.
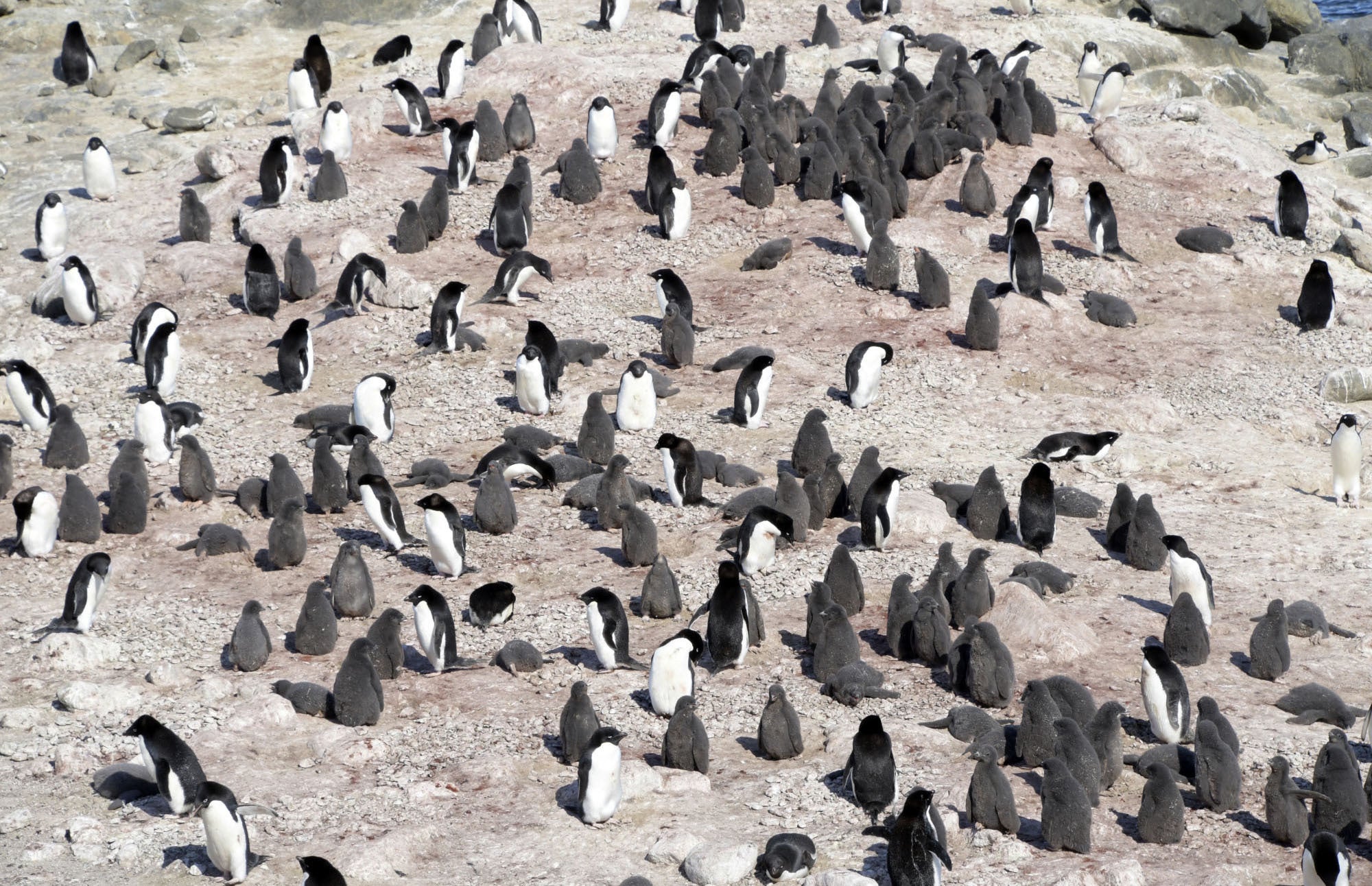
Lynch is affiliated with two diverse citizen-science assignments aimed at improved comprehension penguins, which, pay attention, we know are not in space. A person of those assignments, called Penguin Observe and available listed here, enlists individuals to discover the birds in photos taken immediately in the vicinity of their colonies. But the other relies on satellite imagery to discover these colonies.
Penguins are so, hmm, productive, that biologists come across the birds by combing by means of satellite imagery hunting for swaths of their poop, which experts contact guano. “So we can map out how substantially space is coated in guano, and that gives us a genuinely fantastic estimate of how many penguins were being truly at the colony at that individual place,” Lynch stated.
Such estimates are useful data that’s otherwise hard to get, she stated. “Even however penguins are the most charismatic and probably the most apparent wildlife to survey in Antarctica, till lately, we realized reasonably minimal about how many penguins there were being in Antarctica and how their abundance was dispersed for the reason that surveying Antarctica is so hard.”
That is wherever the satellites arrive into participate in. Lynch and her colleagues use data gathered by a handful of diverse styles of orbital techniques. Commercial satellites provide data that is really comprehensive, NASA’s Landsat program offers a forty-yr viewpoint on penguin functions and Google Earth pulls in publicly available satellite data that citizen experts can comb by means of.
It is that data that supports Lynch’s Mapping Software for Penguin Populations and Projected Dynamics project. The most important target of the initiative is to provide Antarctic policymakers with additional detailed data about penguin populations in 1 location. But the experts will need enable finding all those birds, and for that, they enlist what they contact penguin detectives.
“The citizen science section of this arrives in for the reason that there is just so substantially of Antarctica,” Lynch stated. “The way that we come across penguin colonies is by and massive by means of handbook browsing of imagery: picture just after picture, foot by foot, scanning the coastline for proof of penguin guano.”
And the uncooperative buggers sometimes relocate with no bothering to notify the experts hunting for them. “Every time we feel that we have observed all the penguin colonies,” Lynch stated, “we quickly find out that we come across additional, or that new colonies are remaining set up around time, for the reason that of local climate adjust, for illustration.”
And preserving an correct map of penguin colonies is vital if people want to enact procedures that retain the tuxedoed birds risk-free. For illustration, Lynch and her colleagues surveying Landsat imagery spotted some colonies of Adelie penguins on what is termed the Danger Island archipelago.
When they visited the space to observe up on those observations, they observed additional penguins than they had ever imagined, even however they imagined they’d observed all the Adelie colonies in Antarctica. “In reality, these were being some of the largest Adelie penguins colonies in the entire world,” Lynch stated. “It was this sort of undiscovered hotspot of Adelie penguins.”
That discovery has been passed along to policymakers who are choosing wherever to draw the borders of a maritime guarded space in the region. “It was exactly that kind of effects that we want to have,” Lynch stated.
But if penguin poop, even penguin poop from space, does not audio like your factor, here’s an choice: examine out some bizarre-hunting galaxies. You can do that by means of one more citizen-science project, called Galaxy Zoo.
The application has been around for additional than a decade, enlisting volunteers to classify the shapes of galaxies. That is the sort of process that any individual can do. “You never even will need to know what a galaxy is,” Chris Lintott, an astrophysicist at the College of Oxford, advised Place.com. And whilst the shape isn’t hard to figure out, it is useful details to have.
“The shape of a galaxy tells you about its history: it tells you about when it accreted content, when it collided with other galaxies, when it fashioned stars and all types of other issues,” Lintott stated. “But astronomers are really fantastic at obtaining photos of galaxies and considerably less fantastic at sorting by means of the data.” For this reason, turning to the community. After a quick coaching session, volunteers are turned loose on the scientists’ source of photos.
“We never will need individuals to invest hours thinking about a individual process except if they want to, just a guess and you get one more galaxy,” Lintott stated. “Many individuals explain it as a little bit like ingesting a packet of chips. You acquire 1, you acquire one more, you acquire one more, and you can surf your way by means of the universe that way.”
And lately, the project instituted a new twist that makes certain issues keep interesting. Though the Galaxy Zoo project was born of the premise that people were being improved at classifying galaxies than computers, 12 a long time has transformed the match a little bit. Now, the project has additional an algorithm, which usually takes treatment of the galaxies that are easiest to classify and saves the stranger kinds for contributors.
Identifications made by Galaxy Zoo volunteers have lately authorized experts to figure out that black holes at the heart of galaxies grow steadily, not by means of collisions of the buildings around them.
Getting people involved in the course of action is useful, Lintott stated, for the reason that of their willingness to see issues an algorithm might not. “People get distracted, and they’re distracted along the way by the unexpected and the uncommon,” Lintott stated. “We’ve observed new styles of galaxy and new types of issues in the sky for the reason that any person who was having section in the project did a really human factor and just stated, ’This is uncommon. I never know what this is.’”
And for the reason that the application pulls data immediately from observatory programs, bringing contemporary photos to the web page, there is usually anything new to see. “You might well be the to start with particular person ever to see that galaxy,” Lintott stated. “Just by logging onto the internet site, you can pretty much see anything that no 1 has ever found before.”
Copyright 2020 Place.com, a Foreseeable future enterprise. All legal rights reserved. This content might not be posted, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.