SMART researchers develop gelatin microcarrier for cell production | MIT News
Scientists from Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technological know-how (Good), MIT’s analysis enterprise in Singapore, have designed a novel microcarrier for significant-scale cell production and enlargement that presents increased generate and cost-success in comparison to classic procedures, and decreases actions essential in the mobile retrieval process. Microcarriers are particles applied in bioreactor-centered cell manufacturing of anchorage-dependent cells.
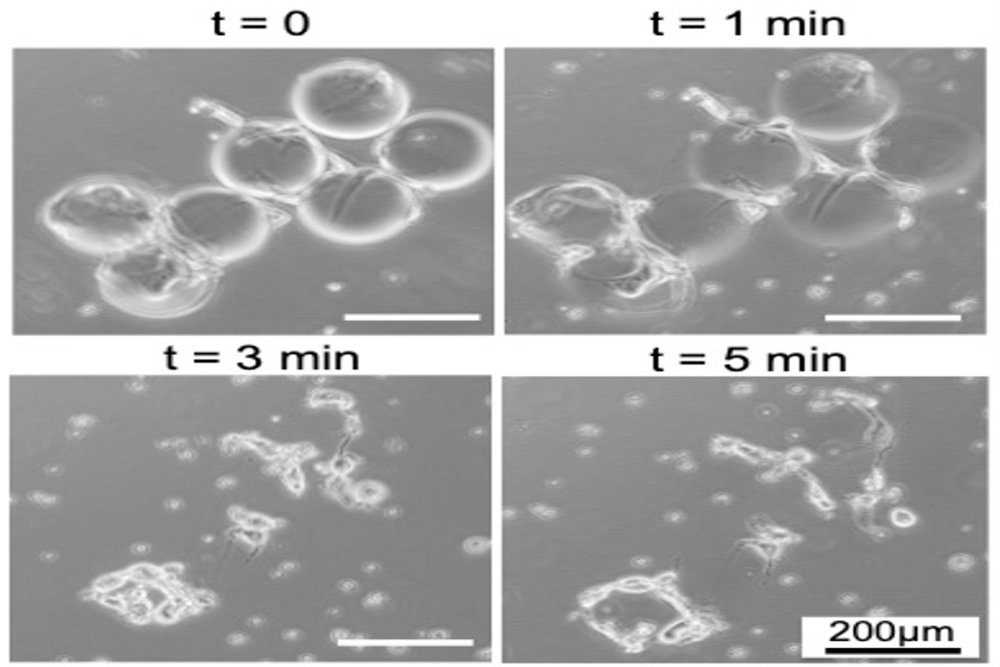
SMART’s newly developed dissolvable gelatin-based microcarrier has confirmed practical for enlargement of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs), a cell kind of great existing desire, as they can be isolated from adult tissues and even further expanded to address several ailments these kinds of as bone and cartilage flaws and the body’s rejection of international bone-marrow and cells (known as graft vs. host condition). This dissolvability of the microcarriers also removes an extra separation step to retrieve the cells from the microcarriers. This cuts down the complexity of mobile manufacturing and rising the simplicity with which the therapeutic cells can be harvested to make the product or service for individuals.
SMART’s Critical Analytics for Production Personalized-Medicine (CAMP) Interdisciplinary Investigate Team (IRG) uncovered that gelatin microcarriers, which completely dissolve in enzymatic procedure, can be practical in the mobile restoration move — one particular of the current bottlenecks confronted in 3D microcarrier tradition. The novel gelatin microcarrier showed higher generate and reduced mobile loss at the mobile harvesting phase when compared to professional microcarriers, with equivalent mobile attachment effectiveness and proliferation charge.
Their discovery is stated in a paper titled “Dissolvable gelatin-dependent microcarriers produced by means of droplet microfluidics for expansion and society of mesenchymal stromal cells” revealed in Biotechnology Journal and co-authored by scientists from Clever CAMP, MIT, Countrywide University of Singapore, and City University of Hong Kong.
“Our research accomplished in excess of 90 per cent harvest level of cells grown on the gelatin microcarriers, which is drastically increased than the 50-60 p.c harvest rate witnessed in current criteria,” states Ee Xien Ng, guide writer of the paper and CAMP alumnus. “Using gelatin microcarriers also attained limited manage more than microcarrier proportions (for illustration, microcarrier diameter and stiffness) that aid uniform environmental problems for managing dependable mobile figures for each microcarrier.”
The research also confirmed that MSCs cultured by gelatin microcarriers retain vital high quality characteristics of retrieved cells, these kinds of as a bigger diploma of trilineage multipotency with more well balanced differentiation performance when compared to professional microcarriers. Most commercial microcarriers showed related trends in adipogenic differentiation efficiency, though losing some levels of chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiation capacity.
“Innovations in microcarriers will support in the scalability of certain mobile styles, this kind of as mesenchymal stromal cells for cell-based therapy, together with for regenerative medication programs,” states Professor Krystyn J. Van Vliet, co-creator of the paper, as properly as lead principal investigator at CAMP and professor of elements science and engineering and biological engineering at MIT. “Developing a microcarrier platform for MSC society has been a crucial section for Wise CAMP’s knowing and running the essential high-quality characteristics of these cell therapy goods. We hope our results enable deliver about much better, far more economical, and scalable cell therapies with predictable therapeutic outcomes for various patient desires, and significant harvesting effectiveness of people strong cells.”
Whilst the examine focused on no matter if gelatin microcarriers are suited for MSC lifestyle and enlargement, the team’s study could probably be prolonged for other sorts of anchorage-dependent cells.
The study is carried out by Smart and supported by the National Study Basis (NRF) Singapore below its Campus for Investigate Excellence And Technological Organization (Make) program.
Clever was proven by MIT in partnership with the Nationwide Exploration Basis of Singapore (NRF) in 2007. Smart is the 1st entity in Develop and serves as an intellectual and innovation hub for study interactions between MIT and Singapore. Intelligent now comprises an Innovation Heart and 5 IRGs: CAMP, Antimicrobial Resistance, Disruptive & Sustainable Systems for Agricultural Precision, Long term Urban Mobility, and Very low Power Digital Methods.
CAMP was launched in June 2019. It focuses on far better ways to develop residing cells as medicine, or cellular therapies, to present much more people obtain to promising and accredited therapies. The investigators at CAMP handle two crucial bottlenecks struggling with the creation of a range of potential cell therapies: vital high quality attributes (CQA) and approach analytic systems (PAT). Leveraging deep collaborations within Singapore and MIT in the United States, CAMP invents and demonstrates CQA/PAT abilities from stem to immune cells. Its function addresses conditions ranging from cancer to tissue degeneration, concentrating on adherent and suspended cells, with and with out genetic engineering.






