Cosmonaut Brain Scans Show Space Does Weird Things to Motor Skills And Vision
Picture you could throw the best bullseye, but you would have to dress in eyeglasses to do it. That is a trade-off some room travellers may perhaps unwittingly make when they venture off the world.
A study posted Friday examined the brains of 8 male Russian cosmonauts around seven months after they returned from prolonged missions to the Intercontinental Area Station.
The researchers identified small modifications in the cosmonauts’ brains that proposed the males have been far more dexterous but had marginally weaker eyesight.
“They basically obtained some form of new motor talent, like driving a bike,” Steven Jillings, the study’s guide writer, told Business Insider.
The researchers utilised a variety of MRI to deliver 3D visuals of the cosmonauts’ brains.
The scans showed an enhanced amount of money of tissue in the cerebellum: the section of the mind accountable for balance, coordination, and posture (revealed in eco-friendly in the movie beneath).
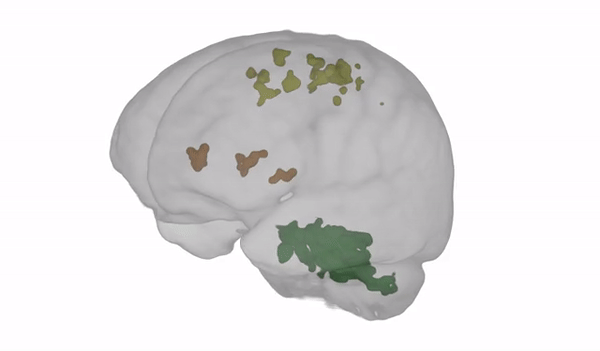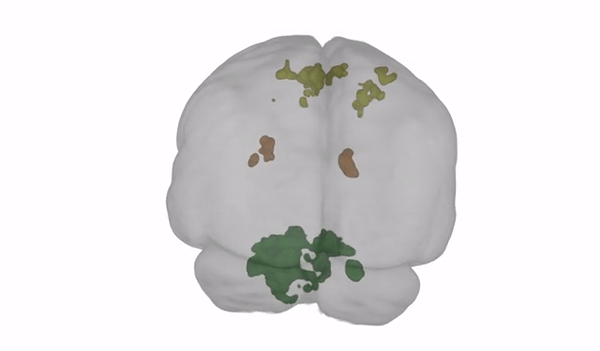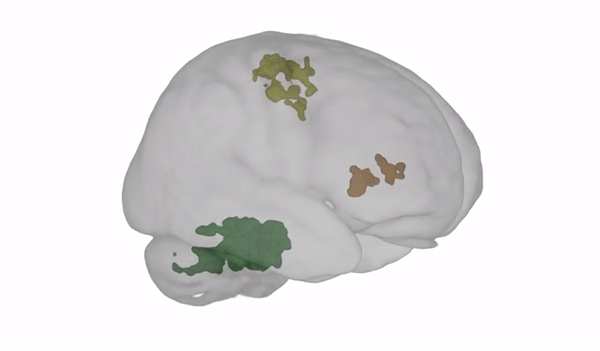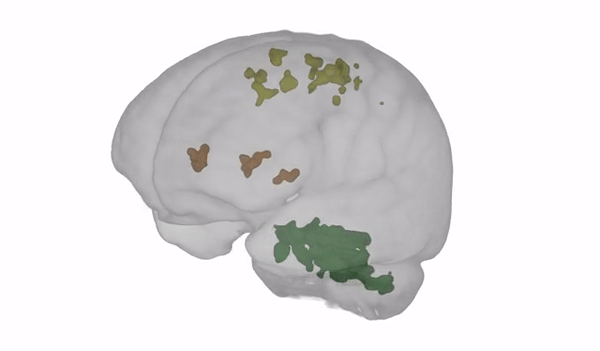 Illustration from Steven Jillings and Ben Jeurissen applying MRtrix3. (University of Antwerp)
Illustration from Steven Jillings and Ben Jeurissen applying MRtrix3. (University of Antwerp)
But the scans also showed that persons dwelling in room could wind up with issues viewing up-shut. Both of individuals modifications could potentially be extensive-lasting.
Changes in motor expertise after room journey
Any human mind, irrespective of whether it has been to room or not, can adapt to new environments and ordeals. A lot of athletes, for occasion, purchase specific motor expertise specifically connected to their activity.
“If you have been to do an MRI study where you look at regular persons to athletes or persons who truly use motor expertise like dart gamers, for instance, you would hypothesize to uncover modifications in the cerebellum,” Jillings reported.
“This is not just for the reason that they properly trained once and then it modifications and goes back again. It really is basically one thing that lasts in the mind.”
On ordinary, the Russian cosmonauts in the study expended 6 months onboard the room station. Researchers envisioned to see non permanent modifications in the cosmonauts’ brains, but they have been surprised to find out that the enhanced motor expertise have been nevertheless there a number of months after they’d returned to Earth.
“The problems with studying these cosmonauts is you really don’t truly have a reference – almost nothing on Earth that it truly can be compared to,” Jillings reported.
“It really is probable that when they go to their up coming mission that they basically are capable to adapt far more promptly.”
Brains shift in room, potentially resulting in blurred eyesight
A lot of preceding scientific studies have revealed that astronauts practical experience physical modifications in microgravity, together with muscle mass and bone reduction.
Astronauts and cosmonauts on the ISS generally training far more than two hours a day to combat this process. They can also come to feel disoriented or motion-unwell although their physique adjusts to a weightless setting.
Just one critical change between existence in room and on Earth is that our blood and bodily fluids typically go versus the downward tug of gravity, whereas in room, astronauts’ bodily fluids shift upward.
The new study observed that microgravity results in the mind to shift upward as well. This in convert redistributes the fluids in which the mind floats.
Jillings reported his study observed proof that the fluid may perhaps pile up driving the eye, resulting in inflammation. This could impair astronauts’ in close proximity to eyesight, resulting in a issue named spaceflight-involved neuro-ocular syndrome.
A 2012 survey observed the same effect amid many NASA astronauts – up to 60 p.c of individuals analyzed reported they have been viewing considerably less evidently onboard the ISS. NASA even flies prescription eyeglasses to room just in scenario an astronaut’s eyesight modifications.
But Jillings reported you can find nevertheless far more to find out about this phenomenon, especially for the reason that not all astronauts or cosmonauts return to Earth with negative eyesight, and most astronauts analyzed only made impaired eyesight in 1 eye. Some also recover their eyesight soon after returning to Earth.
What’s far more, many Russian cosmonauts have really sharp sight to start with, so even after they full a stint in room, their eyesight is nevertheless regular compared to the ordinary person.
“The fact that we do see the little minimize most likely suggests that there are some common outcomes throughout all persons who spend 6 months in room,” Jillings reported.
Researchers are nevertheless seeking to establish the diploma to which the impaired eyesight could be long lasting.
An April study from the University of Texas observed that inflammation in astronauts’ brains persisted 1 12 months after their return to Earth. But Jillings reported there are no extensive-phrase abide by-up scientific studies to see how extensive the issue truly lasts over and above that.
“There are not many scientific studies hunting into the brains of astronauts,” he reported.
In general, Jillings added, it truly is good information that his study failed to pick up on any really serious health outcomes linked to room journey.
Previous scientific studies, by contrast, have proposed that radiation in room could guide to neurodegeneration, which may well accelerate the enhancement of Alzheimer’s disease amid astronauts.
“We did not uncover any proof of detrimental modifications to the mind,” Jillings reported. “It really is basically far more of an adaptation.”
This report was initially posted by Business Insider.
Extra from Business Insider:




