Scientists Discover Extremely Tiny Dinosaur Ancestor in Madagascar
Its identify was Kongonaphon kely, which signifies ‘tiny bug slayer’, and it was about the dimensions of a coffee cup. But large things lay forward for this small creature. Quite large things in truth.
The tiny bug slayer, which lived on Madagascar roughly 237 million decades in the past throughout the Triassic time period, stood just ten centimetres (about 4 inches) tall. Even so, scientists say K. kely belonged to the ancient group Ornithodira: the last typical ancestor of all the dinosaurs and pterosaurs that would one particular working day reign in the bug slayer’s wake.
“There is certainly a general perception of dinosaurs as remaining giants,” claims palaeontologist Christian Kammerer from the North Carolina Museum of All-natural Sciences.
“But this new animal is pretty close to the divergence of dinosaurs and pterosaurs, and it is really shockingly modest.”
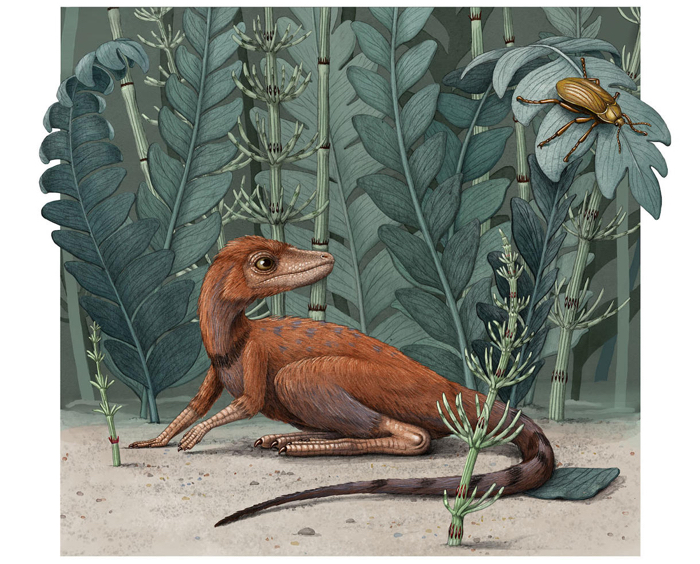 Artist’s perception. (Alex Boersma)
Artist’s perception. (Alex Boersma)
How did this kind of colossal creatures evolve from this kind of unassuming origins? The reply has never ever been fully distinct, due to the fact rather couple of specimens from the root lineage of Ornithodira have ever been learned and analyzed.
That’s why the bug slayer’s old bones are so crucial. They were 1st found throughout subject operate in 1998 at a fossil internet site in southwestern Madagascar, alongside with the continues to be of hundreds of other ancient specimens.
“It took some time prior to we could target on these bones, but at the time we did, it was distinct we experienced anything special and worthy of a nearer glimpse,” claims palaeontologist John Flynn from the American Museum of All-natural Historical past.
K. kely is the smallest identified species in a household of early dinosauromorphs termed Lagerpetidae. These early examples of Ornithodira are identified to be modest, but with recent discoveries this kind of as the tiny bug slayer, scientists are coming spherical to the plan that the smallness of learned specimens is no accident.
“Though dinosaurs and gigantism are pretty much synonymous, an examination of human body dimensions evolution in dinosaurs and other archosaurs in the context of this taxon and connected types demonstrates that the earliest-diverging associates of the group may possibly have been lesser than beforehand believed, and that a profound miniaturisation function transpired around the base of the avian stem lineage,” the group writes in a new paper.
 (Phylopic.org by Scott Hartman [CC BY three.] & Frank Ippolito/AMNH)
(Phylopic.org by Scott Hartman [CC BY three.] & Frank Ippolito/AMNH)
Earlier mentioned: Human body dimensions comparison between Kongonaphon kely, and early dinosaur Herrerasaurus.
Evidence to assist this will come in the variety of the tiny bug slayer’s teeth and pitted abrasions on them, steady with a eating plan of tough-shelled bugs, the group claims. If they are proper, it is really probable that these lesser dinosaur and pterosaur ancestors adapted their diminutive frames to “invade useful resource zones not beforehand occupied by archosaurs” as a form of evolutionary edge.
In carrying out so, it is really also probable that the change to this tiny human body served K. kely and its archosaur peers unlock and build other traits that would go on to come to be a mainstay of their descendants’ survival: innovations in bipedal motion, the origins of fluff to warm modest bodies, and even the beginnings of flight, the scientists suggest.
The tiny bug slayer failed to get to see or take pleasure in all that for by itself, of program. But all those formidable tomorrows experienced some of their beginnings in this article.
The results are noted in PNAS.




